Author: Sic
CRISPR
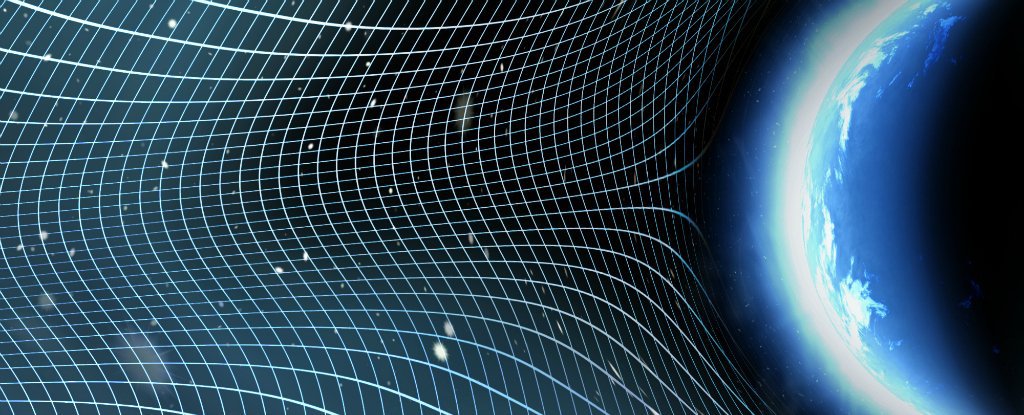
If you’re a scientist who works with genes, it has already rocked your world: You can now snip an unwanted gene out of a DNA strand and replace it with another. Unlike the expensive blitz approaches of previously developed gene therapies, CRISPR techniques allow scientists to zero in on and knock out one problematic sequence. A process that used to be difficult, slow and haphazard has become a whole lot easier, faster and cheaper, opening up applications from medicine to agriculture. As journalist Carl Zimmer says: “Nobody’s found any place where it doesn’t work.”
via What’s wrong with scientists trying to use CRISPR to fix everything? |.
researchers have claimed to detect a fifth force (there’s even a Wikipedia page for fifth force possibilities), but the search has really heated up over the past decade. Many scientists think there might be a particle out there called a ‘dark photon’, which could carry a new force that would explain dark matter – that invisible substance that makes up more than 80 percent of the Universe’s mass.
That’s what the Hungarian team, led by physicist Attila Krasznahorkay, were looking for. To do that, they fired protons at thin targets of lithium-7, a collision that created unstable beryllium-8 nuclei, which then decayed into pairs of electrons and positrons.
“According to the standard model, physicists should see that the number of observed pairs drops as the angle separating the trajectory of the electron and positron increases,” Edwin Cartlidge writes for Nature.
But that wasn’t what the team saw – at about 140 degrees, the number of these pairs jumped, creating a little bump before dropping off again at higher angles.
This ‘bump’ was evidence of a new particle, according to Krasznahorkay and his team. They calculated that the mass of this new particle would be around 17 megaelectronvolts, which isn’t what was expected for the ‘dark photon’, but could be evidence of something else entirely.
http://www.sciencealert.com/physicists-think-they-might-have-just-detected-a-fifth-force-of-nature
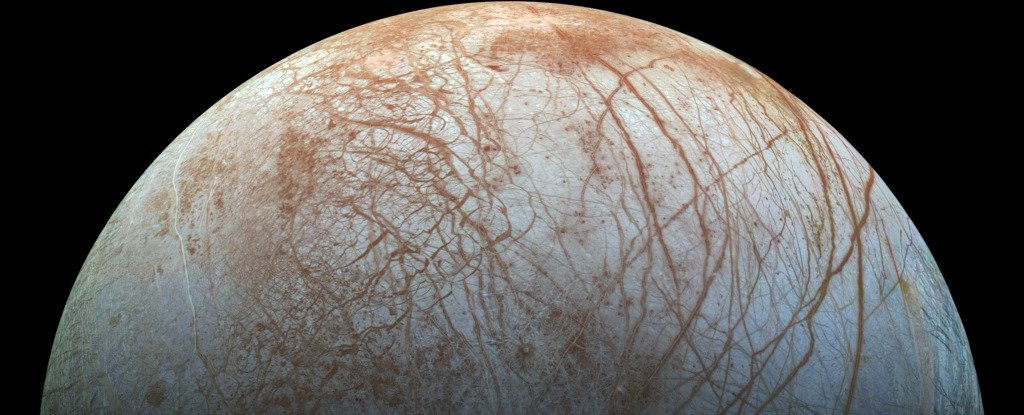 Scientists just found even more evidence that Europa – one of Jupiter’s 67 known moons – might host alien life deep within its icy oceans. The little moon has long been labelled by NASA as “the most likely place to find life in our Solar System today“, thanks to the deep, salty oceans that are strongly suspected to be hidden beneath its frozen crust.
Scientists just found even more evidence that Europa – one of Jupiter’s 67 known moons – might host alien life deep within its icy oceans. The little moon has long been labelled by NASA as “the most likely place to find life in our Solar System today“, thanks to the deep, salty oceans that are strongly suspected to be hidden beneath its frozen crust.
And now a new study has shown that the chemical balance of those oceans would be very similar to the ones here on Earth, suggesting there’d be enough hydrogen and oxygen there for life to form – even without volcanic activity.
http://www.sciencealert.com/nasa-just-found-even-more-evidence-that-europa-could-host-alien-life
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y87Qk34BZUQ
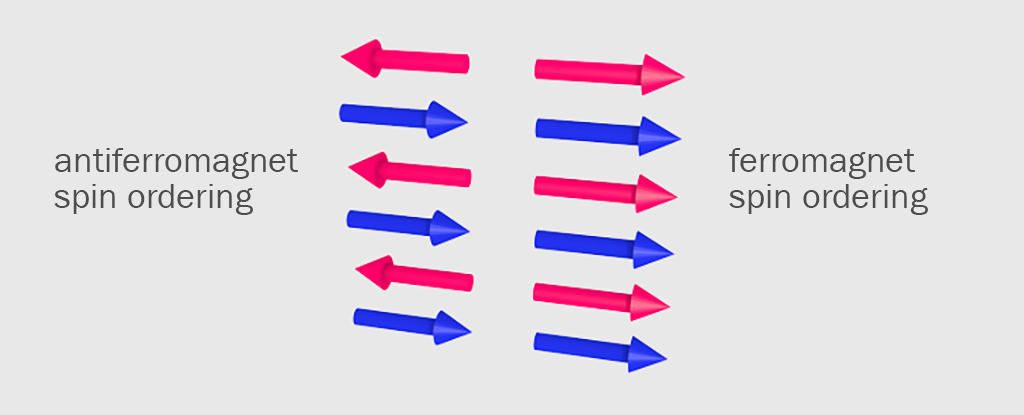
Basically, the spin of electrons rather than their charge is used to map out the 1s and 0s of our data.Diamond Light SourceThat’s the science, but here are the main benefits. First of all, there’s no density change in the current compared with the data storage devices we use today, so upgrading should become easier. Secondly, the antiferromagnetic materials don’t emit an external magnetic field, so there’s less chance of devices interfering with other equipment or being spied on.A lack of magnetic field also means individual regions can be packed very close together, giving us more data in less space. Information can also remain intact without power, and can be written and read at room temperature – all boxes that need ticking when you’re investigating the potential of a next-generation storage technology.The spintronics approach has the potential to increase read and write times by a factor of up to 1,000
via New ‘spintronics’ technology is set to offer a huge leap forward in data storage – ScienceAlert.
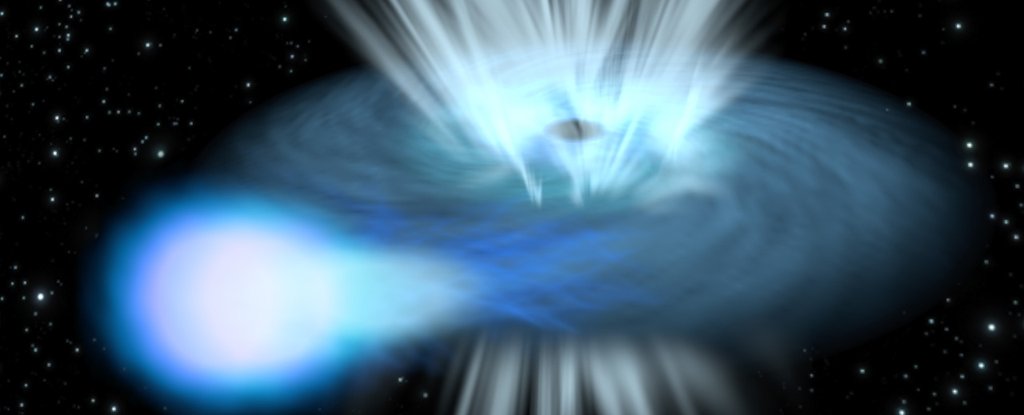

Astronomers have found two black holes that are blasting out gas at speeds up to a quarter of the speed of light – and are breaking the currently accepted laws of physics in the process.